Welcome to the PerGeos Use Case Gallery
Below you will find a collection of use cases using PerGeos Software. Based on the technology of its predecessor Avizo Software, PerGeos is a robust software platform for visualizing, processing, and analyzing 2D and 3D digital rock image data.
These use cases include scientific publications, articles, papers, posters, presentations or even videos that show how PerGeos is used to address various scientific and industrial research topics.
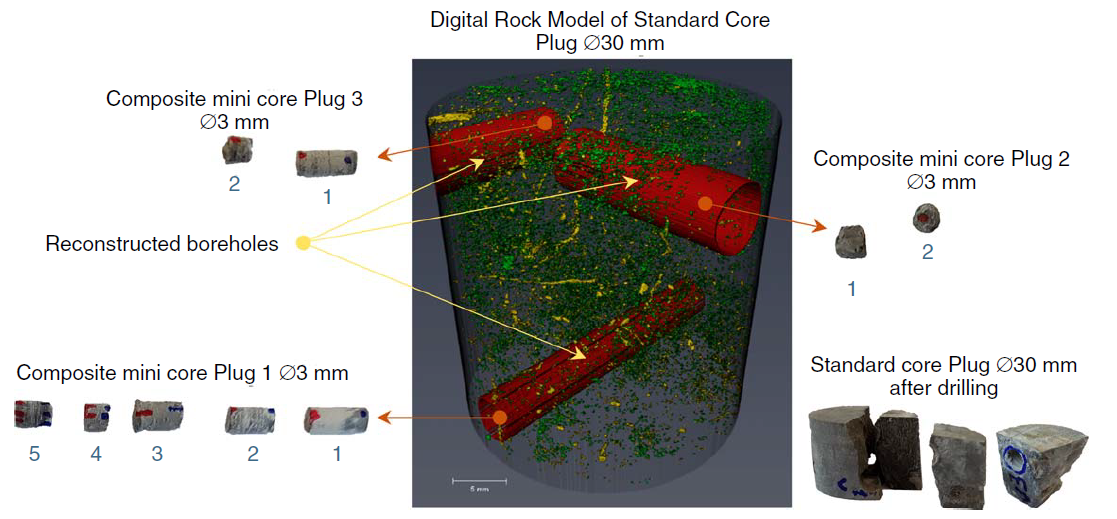
The task of reliable characterization of complex reservoirs is tightly coupled to studying their microstructure at a variety of scales, which requires a departure from traditional petrophysical approaches and delving into the world of nanoscale. A promising method of representatively retaining a large volume of a rock sample while achieving nanoscale resolution is based on multiscale digital rock technology. The smallest scale of this approach is often realized in the form of working with sev... Read more
Andrey Kazak - Svyatoslav Chugunov - Anatolii Chashkov
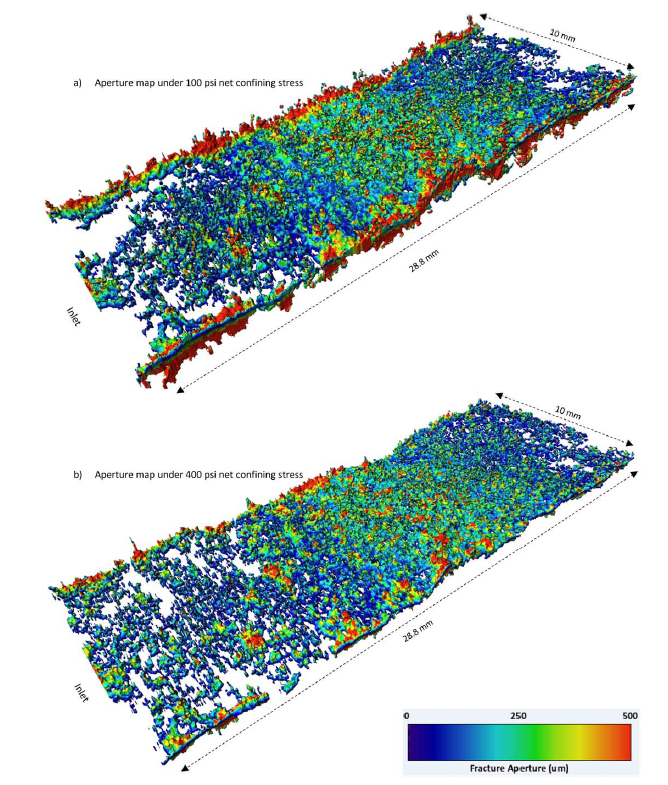
Pore‐Scale Experimental Investigation of Two‐Phase Flow Through Fractured Porous Media
Understanding transport mechanisms that govern two-phase flow in fractured porous media has direct implications for natural and industrial processes such as extraction of hydrocarbons from fractured reservoirs, geologic sequestration of CO2, or fluid flow through aquifers.
We present the results of a systematic pore‐scale experimental investigation of two‐phase oil/brine flow through a miniature water‐wet, fractured sandstone core sample. X‐ray microtomography is employed to ge... Read more
M. Arshadi, M. Khishvand, A. Aghaei, M. Piri, G. A. Al‐Muntasheri
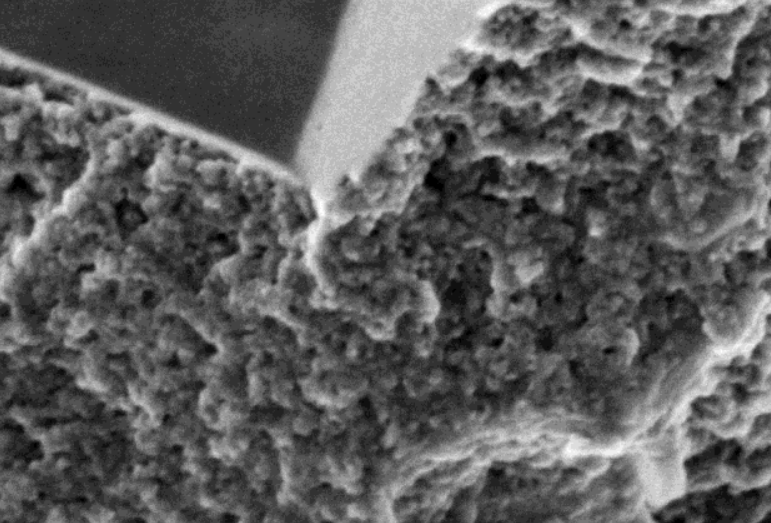
Optimization of production from shale reservoirs requires understanding of rock properties over a range of scales.
Multiple imaging techniques can be combined to determine the nature, connectivity, and wettability of nano-scale pore systems as well as the underlying mineralogy and organic textures that control reservoir behavior and the propensity of the matrix to fail and to contain expulsion cracks. The current study demonstrates new capabilities in integrated multiscale and time-res... Read more
Andrew Fogden, Alession Arena, Christopher Zhang, Ryan T. Armstrong
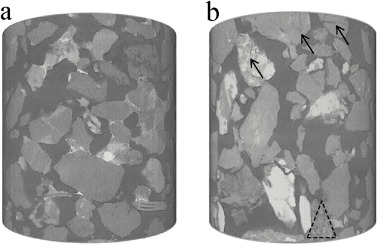
This study investigated the influence of compaction on the variation mechanism of petrophysical properties and the relative permeability of unconsolidated sandstone.
Firstly, triaxial mechanical experiments, CT scans, and mercury injection experiments were performed to analyze the microstructural characteristics and the macroscopic mechanism of changes in the petrophysical characteristics under different pressure. Secondly, a modified permeability test approach was adopted on reservoir... Read more
Yu Xiong, Hongguang Xu, Yongqing Wang, Wensheng Zhou, Ling Wang, Kai Feng
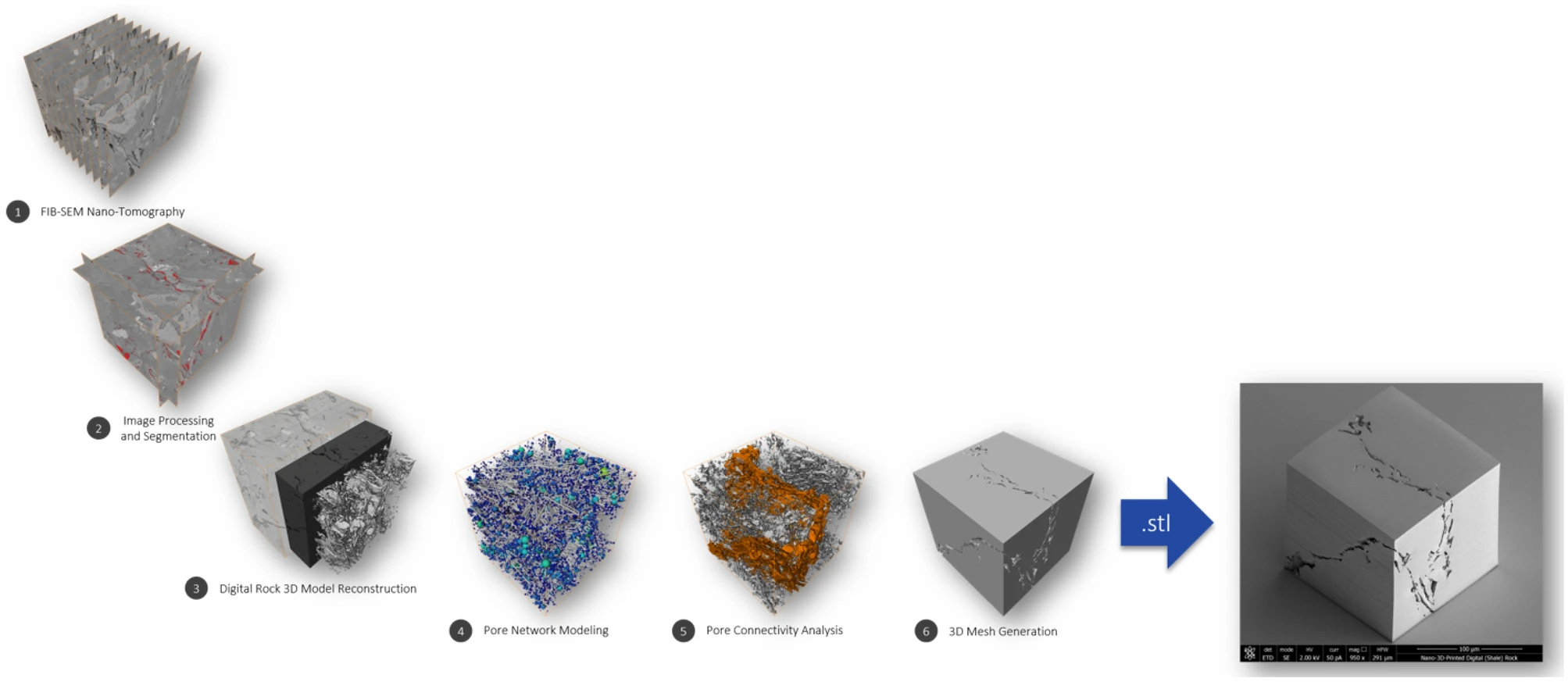
Advances in imaging have made it possible to view nanometer and sub-nanometer structures that are either synthesized or that occur naturally. It is believed that fluid dynamic and thermodynamic behavior differ significantly at these scales from the bulk. From a materials perspective, it is important to be able to create complex structures at the nanometer scale, reproducibly, so that the fluid behavior may be studied. New advances in nanoscale-resolution 3D-printing offer opportunities to ach... Read more
Jan Goral & Milind Deo
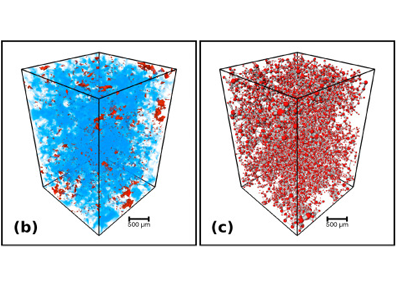
Pore network analysis of Brae Formation sandstone, North Sea
Generating an accurate reservoir model is of critical importance in forecasting the lifespan of hydrocarbon reservoirs and estimating the efficiency of carbon capture and sequestration. One critical parameter controlling the flow of fluids within subsurface reservoirs is the fraction of effective or connected pore spaces in the reservoir. […]
To quantify the connectivity of the pore space, it is therefore necessary to combine high resolution visualization of pore spaces with bulk... Read more
Paul-Ross Thomson; Mark Jefferd; Brett L. Clark; Domenico Chiarella; Tom Mitchell; Saswata Hier-Majumder
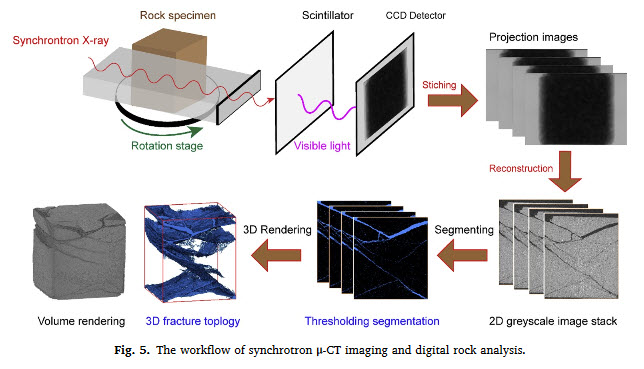
Dynamic strength and failure modes of sandstone under biaxial compression
Geomaterials are increasingly being subjected to the quasi-static confinements and dynamic loadings, and thus it is critical to characterise dynamic behaviour under the coupled static-dynamic loading conditions. In this study, a series of dynamic biaxial compression tests was performed on cubic specimens of sandstone by using a triaxial Hopkinson bar system, high-speed three-dimensional digital image correlation (3D-DIC) and synchrotron-based micro-computed-tomography (μCT).
Read more
K. Liua, J. Zhaoa, G. Wua, A. Maksimenkob, A. Haquea, Q.B. Zhang
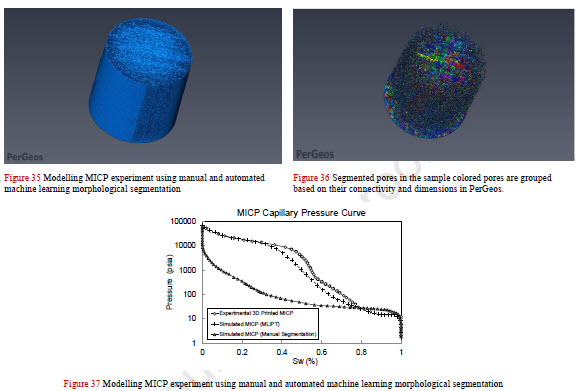
Experimental Investigation of 3D Printed Rock Samples Replicas
Laboratory Experiments on rock specimens are designed for understanding and characterizing subsurface environment, quantifying potential recovery, and tuning fluid flow models in porous media. The spatial variability and reservoirs’ heterogeneities predicate acquiring expensive cores from different locations. These experiments are mechanically and petrophysically destructive and cannot be repeated or extended on the same core. Replicating core samples with 3D-printing technology innovation ... Read more
Ahmed G.Almetwally, H.Jabbari
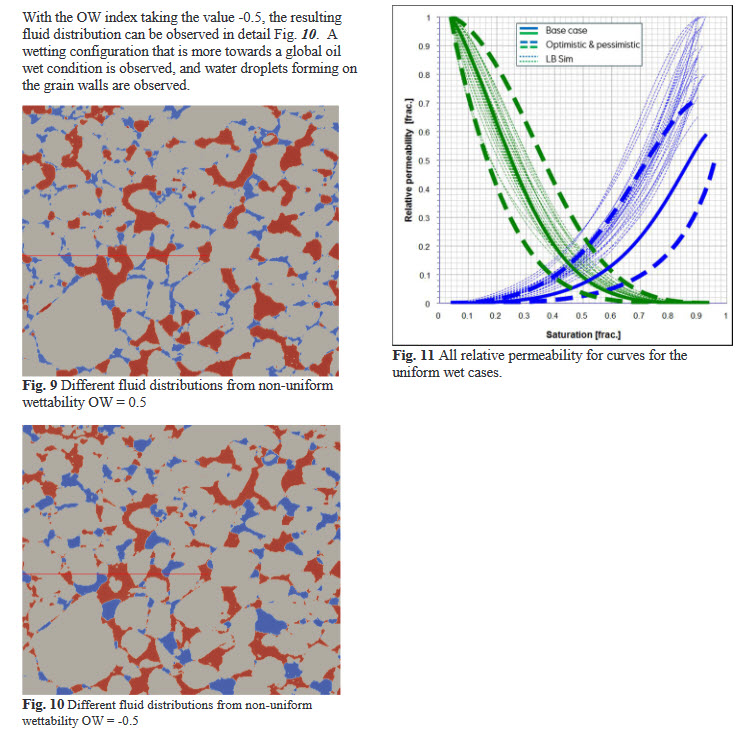
Relative permeability and capillary pressure are key properties within special core analysis and provide crucial information for full field simulation models. These properties are traditionally obtained by multi-phase flow experiments, however pore scale modelling has during the last decade shown to add significant information as well as being less time-consuming to obtain. Pore scale modelling has been performed by using the lattice-Boltzmann method directly on the digital rock models obtain... Read more
ThomasRamstad, Anders Kristoffersen, and EinarEbeltoft
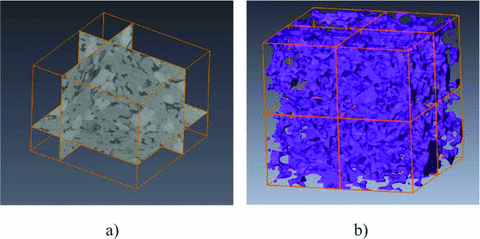
Computational elastic upscaling of sandstone on the basis of X‐ray micro‐tomographic images
Up‐scaling the elastic properties of digitized rock volumes as obtained from X‐ray computer tomography (CT) imaging via computer simulations has the potential to assist and complement laboratory measurements.
This computational up‐scaling approach remains a challenging task as the overall elastic properties are not only dependent on the elastic properties of individual grains but also on the hardly resolvable pore spaces between adjacent grains such as micro‐cracks. We develop ... Read more
Valeriya Shulakova, Marina Pervukhina, Tobias M. Müller, Maxim Lebedev, Sherry Mayo, Susanne Schmid, Pavel Golodoniuc, Osni Bastos De Paula, Michael B. Clennell, Boris Gurevich
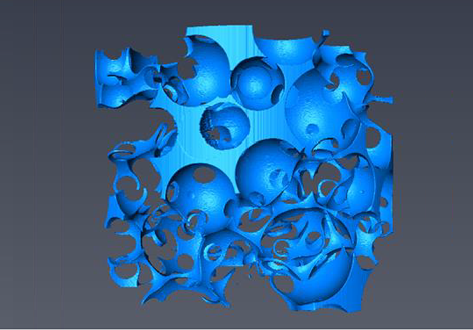
In this study, we examined the relationship between capillary pressure, saturation, and interfacial area for a three-phase flow system. Using x-ray microtomography we were able to capture high-resolution three-dimensional images of the flow system, from which the saturation, interfacial area, and capillary pressure were determined.
Multi-phase flow in porous media includes many instances of subsurface flow. Three-phase flow in particular is important in situations of enhanced oil recov... Read more
Rebecca Paustian
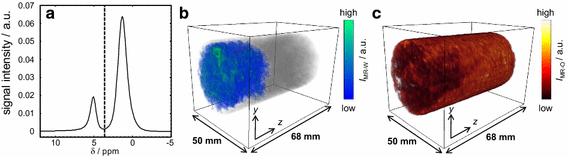
Accurate monitoring of multiphase displacement processes is essential for the development, validation and benchmarking of numerical models used for reservoir simulation and for asset characterization.
Here we demonstrate the first application of a chemically-selective 3D magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) technique which provides high-temporal resolution, quantitative, spatially resolved information of oil and water saturations during a dynamic imbibition core flood experiment in an Esta... Read more
N. P. Ramskill, A. J. Sederman, M. D. Mantle, M. Appel, H. de Jong, L. F. Gladden
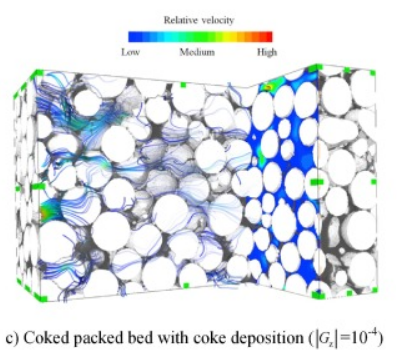
Coke deposition during crude oil in-situ combustion (ISC) is an important phenomenon that significantly impacts the pore topology and permeability.
In this study, X-ray computed microtomography and a specific image processing procedure were used to reconstruct the micro-tomographic images of packed beds with coke deposition. From the reconstructed images, the microstructural parameters related to the transport were analyzed, such as the effective porosity, the constrictivity and the ge... Read more
Qianghui Xu, Wei Long, Hang Jiang, Bin Ma, Cheng Zan, Desheng Ma, Lin Shi
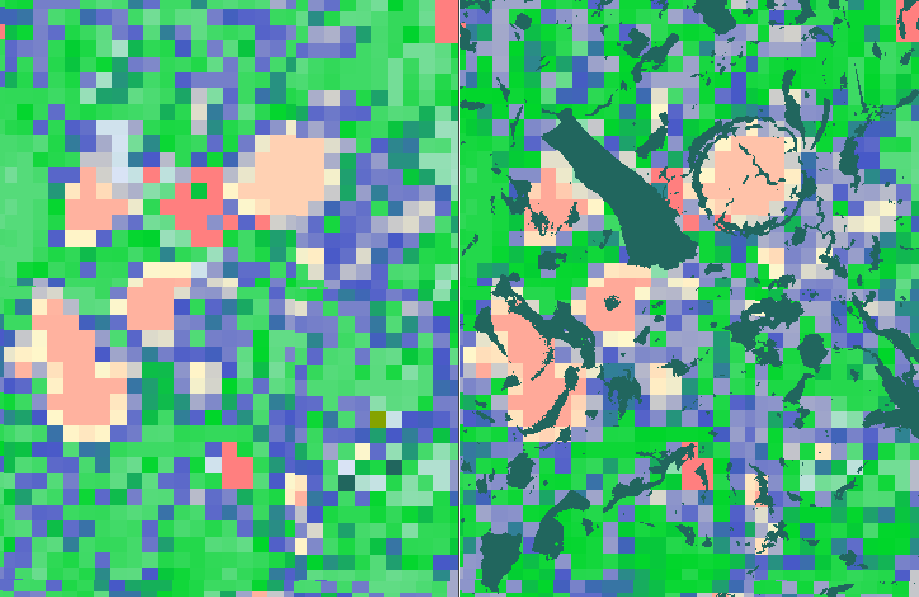

A Bridge With MAPS Mineralogy PerGeos v1.7
With the introduction of the Maps Mineralogy™ software suite, the successor of Qemscan, the technology has evolved, thanks to multiple patents bringing novel methods to acquire mineralogical information from digital rock samples with a modern and user friendly interface.
However, given the hardware technology advances and the emergence of new challenges in reservoir rocks, there is a need to fusion the mineralogical image and the back scattered electron... Read more
Gwenole Tallec - Thermo Fisher Scientific

Handling Large data in PerGeos
We introduce here some techniques to visualize and process large data, mostly targeting the high resolution data acquired by Heliscan microCT.
The data is considered as “large” in the sense that its size exceeds the size of the GPU memory and/or the size of the RAM of the machine.
The following workflow:
- Segmentation
- Porosity / Connected porosity determination
- Pore separation / Pore Size distribution
- Grain size distribution
Gwenole Tallec - Thermo Fisher Scientific
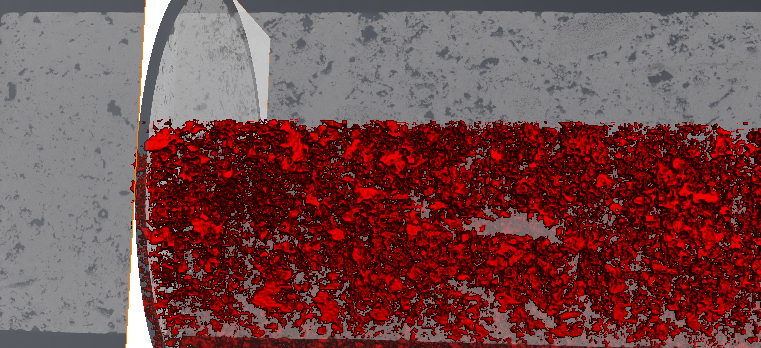
Segmentation tools and workflows in PerGeos
Imagery produced from FIBSEMs (Dualbeams) provides users with unique data in terms of resolution and sample size that are not available with other techniques. Despite the power of this analytical approach, some limitations in quantifying the textural data restrict the accuracy of data obtained from FIBSEM images.
Segmentation typically consists of a complex workflow involving multiple algorithms at multiple steps. Smart denoising and morphological filters are often included in the segm... Read more
Gwenole Tallec - Thermo Fisher Scientific
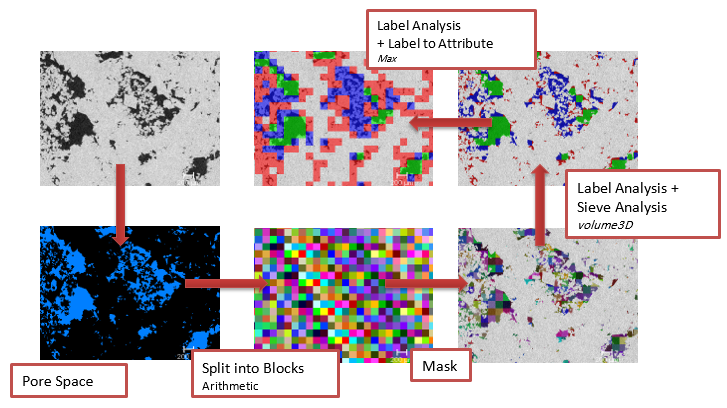
Simple Rock Characterization in PerGeos v1.7
A key benefit to obtaining digital imagery data is the ability to use all parts of the imaged sample for characterization purposes-not just what you have time to explore manually. This is especially the case with large datasets that are created during acquisition of 2D mosaic images or Whole Core CT imagery.
In these cases, a representative area or volume of material has been obtained. The next step will be to extract features, like porosity, for analysis.
But, what else can we ... Read more
Gwenole Tallec - Thermo Fisher Scientific
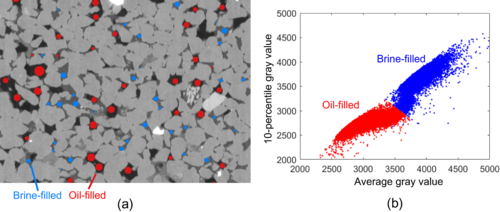
Validation of model predictions of pore-scale fluid distributions during two-phase flow
Pore-scale two-phase flow modeling is an important technology to study a rock’s relative permeability behavior. To investigate if these models are predictive, the calculated pore-scale fluid distributions which determine the relative permeability need to be validated. In this work, we introduce a methodology to quantitatively compare models to experimental fluid distributions in flow experiments visualized with microcomputed tomography.
First, we analyzed five repeated drainage-i... Read more
Tom Bultreys, Qingyang Lin, Ying Gao, Ali Q. Raeini, Ahmed AlRatrout, Branko Bijeljic, and Martin J. Blunt
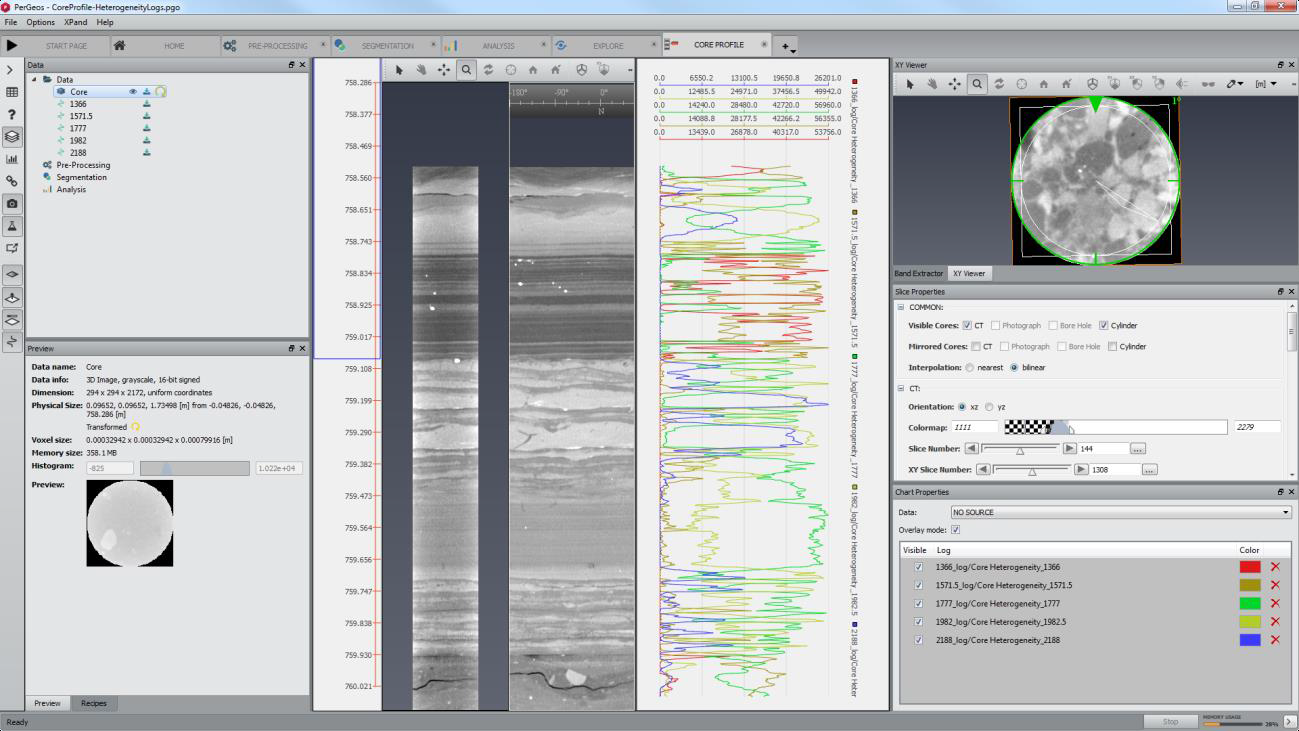
Improving Whole Core Characterization with Automated Log Generation in PerGeos
The Core Profile Extension, available for PerGeos, provides a powerful toolset for visualization and analysis of whole core CT data. Within this extension the user can load and visualize an entire wells worth of CT data as well as performing detailed analysis of geological and chemical features by utilizing the powerful image analysis library fundamental to PerGeos.
In this example, we illustrate the usefulness of core profile in augmenting traditional core analysis routines and provid... Read more
Gwenole Tallec - Thermo Fisher Scientific
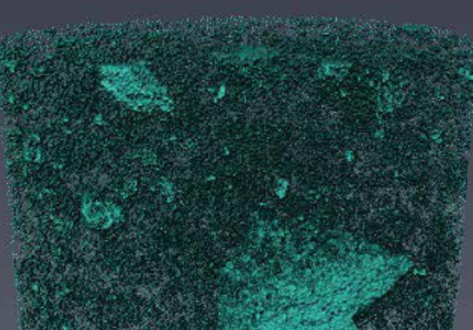
Laboratory Noble Gas Migration Experiments Through Rock
The Underground Nuclear Explosion Signature Experiment (UNESE) is a multi-laboratory effort to improve U.S. capabilities to detect, locate, identify, and characterize underground nuclear explosions. Here we present a lab-scale experiment developed to test advective gas transport though rock samples at in-situ conditions, and results of tests performed at ambient conditions on rocks collected from the site of a field-scale experiment. Gas transport results are compared to pore and fracture net... Read more
Sandia National Laboratories, Los Alamos National Laboratory
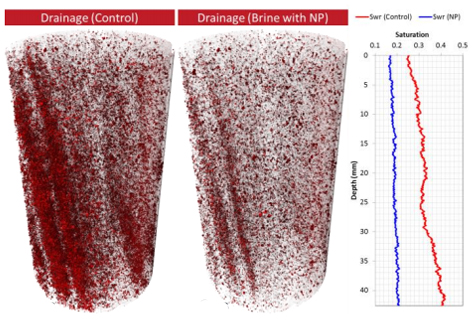
Pore-Scale observations of the effect of surface treated nanoparticles on drainage processes
In this study we observe, using pore scale X-ray micro-CT imaging and advanced petrophysical analysis, how surface treated silica nanoparticles improve sweep efficiency of n-octane in drainage corefloods. Specifically, upon injection of n-octane into a brine saturated core, preferential flow paths are observed and attributed to both viscous instability and rock heterogeneity; when the displaced phase contains a modest volume of nanoparticles, the same preferential flow paths are suppressed re... Read more
Department of Petroleum Engineering, The University of Texas at Austin | Departments of Chemical and Petroleum Engineering, University of Calgary | Materials & Structural Analysis, Thermo Fisher Scientific