Welcome to the PerGeos Use Case Gallery
Below you will find a collection of use cases using PerGeos Software. Based on the technology of its predecessor Avizo Software, PerGeos is a robust software platform for visualizing, processing, and analyzing 2D and 3D digital rock image data.
These use cases include scientific publications, articles, papers, posters, presentations or even videos that show how PerGeos is used to address various scientific and industrial research topics.
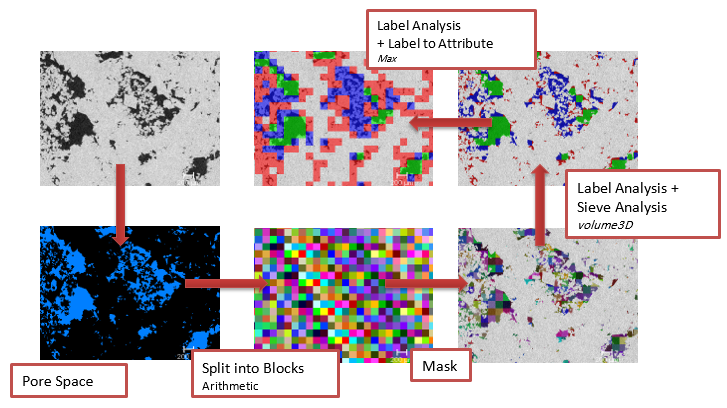
Simple Rock Characterization in PerGeos v1.7
A key benefit to obtaining digital imagery data is the ability to use all parts of the imaged sample for characterization purposes-not just what you have time to explore manually. This is especially the case with large datasets that are created during acquisition of 2D mosaic images or Whole Core CT imagery.
In these cases, a representative area or volume of material has been obtained. The next step will be to extract features, like porosity, for analysis.
But, what else can we ... Read more
Gwenole Tallec - Thermo Fisher Scientific
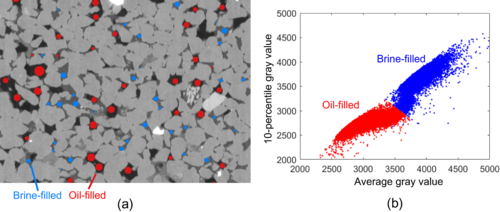
Validation of model predictions of pore-scale fluid distributions during two-phase flow
Pore-scale two-phase flow modeling is an important technology to study a rock’s relative permeability behavior. To investigate if these models are predictive, the calculated pore-scale fluid distributions which determine the relative permeability need to be validated. In this work, we introduce a methodology to quantitatively compare models to experimental fluid distributions in flow experiments visualized with microcomputed tomography.
First, we analyzed five repeated drainage-i... Read more
Tom Bultreys, Qingyang Lin, Ying Gao, Ali Q. Raeini, Ahmed AlRatrout, Branko Bijeljic, and Martin J. Blunt
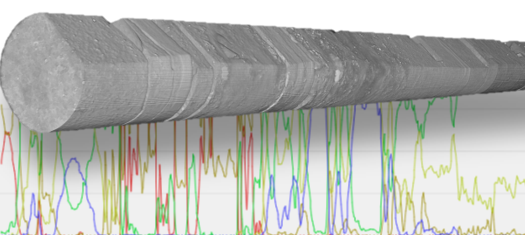
Heterogeneity Logs in PerGeos 1.5
The Core Profile workspace of PerGeos already provides the right tools to visualize logs, CT cores, Bore Hole images and Photographs.
A unique preprocessing step allows the cores barrel to be intelligently removed, the core to be re-oriented if it is not perfectly vertical, and all the cores to be stitched together regardless of the total size.
This allows a user to browse in real time an entire 3D digital well of 100+ cores and apply post-processing operations such as logs gene... Read more
Gwenole Tallec - Thermo Fisher Scientific
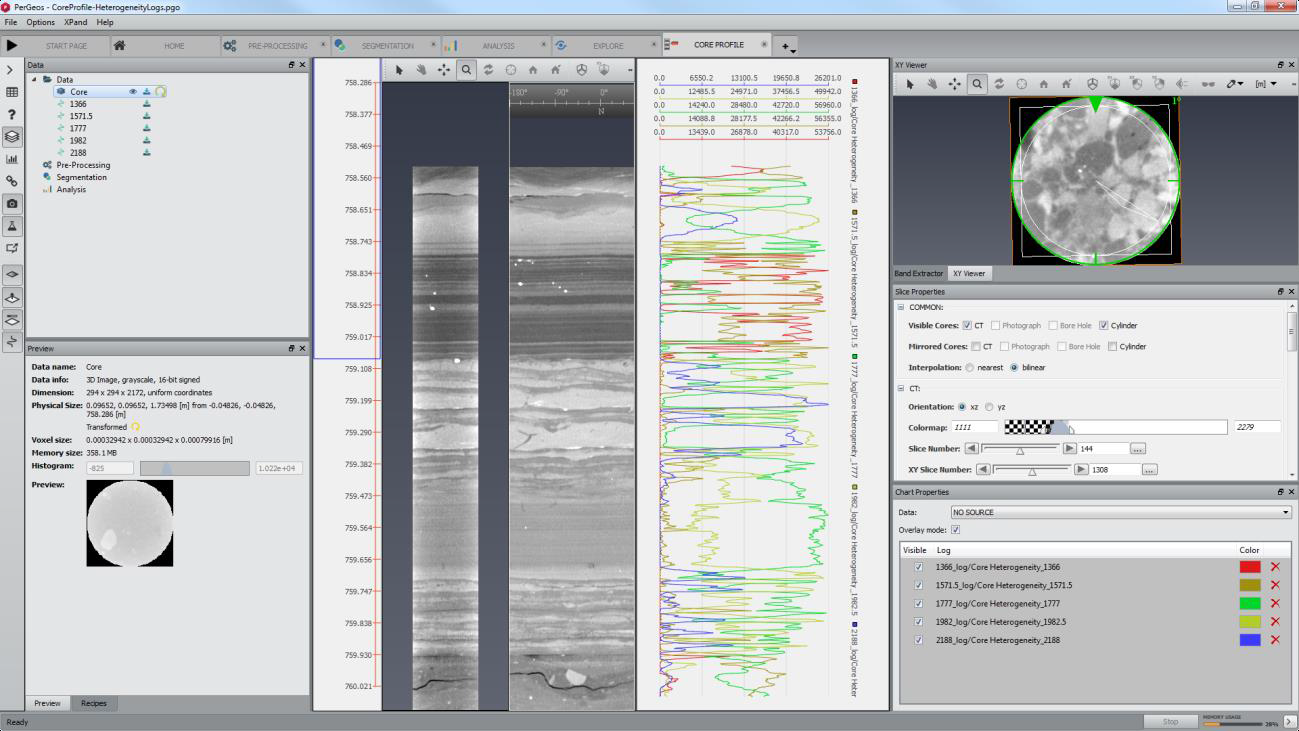
Improving Whole Core Characterization with Automated Log Generation in PerGeos
The Core Profile Extension, available for PerGeos, provides a powerful toolset for visualization and analysis of whole core CT data. Within this extension the user can load and visualize an entire wells worth of CT data as well as performing detailed analysis of geological and chemical features by utilizing the powerful image analysis library fundamental to PerGeos.
In this example, we illustrate the usefulness of core profile in augmenting traditional core analysis routines and provid... Read more
Gwenole Tallec - Thermo Fisher Scientific
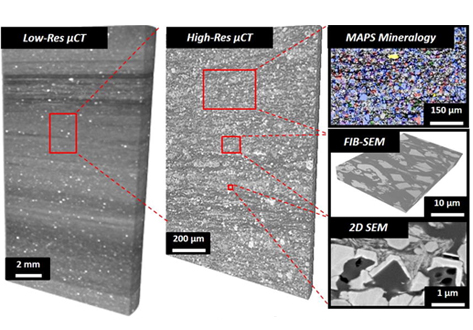
The complexity of unconventional rock systems is expressed both in the compositional variance of the microstructure and the extensive heterogeneity of the pore space. Visualizing and quantifying the microstructure of oil shale before and after pyrolysis permits a more accurate determination of petrophysical properties which are important in modeling hydrocarbon production potential. We characterize the microstructural heterogeneity of oil shale using X-ray micro-tomography (µCT), automated u... Read more
Imperial College London, Tarik Saif, Qingyang Lin, Alan R.Butcher, Branko Bijeljic, Martin J.Blunt
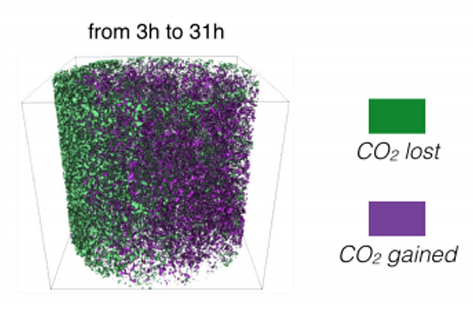
Pore-scale evolution of trapped CO2 at early stages following imbibition using micro-CT imaging
Despite its major influence on storage capacity, CO2 plume migration rate, and rates of CO2 dissolution and mineralization, there are outstanding questions regarding the mechanisms, times scales, influence of geological heterogeneity, and degree of residual trapping. The aim of the present study is to track temporal evolution of residually-trapped scCO2 ganglia during the early stages following imbibition, extract critical parameters such as fluid phase connectivity and scCO2 cluster size an... Read more
Department of Energy Resources Engineering, Stanford University | Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, Earth and Environmental Sciences
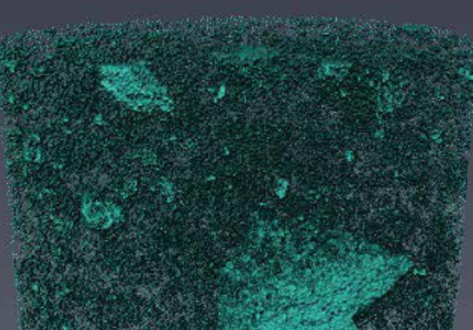
Laboratory Noble Gas Migration Experiments Through Rock
The Underground Nuclear Explosion Signature Experiment (UNESE) is a multi-laboratory effort to improve U.S. capabilities to detect, locate, identify, and characterize underground nuclear explosions. Here we present a lab-scale experiment developed to test advective gas transport though rock samples at in-situ conditions, and results of tests performed at ambient conditions on rocks collected from the site of a field-scale experiment. Gas transport results are compared to pore and fracture net... Read more
Sandia National Laboratories, Los Alamos National Laboratory
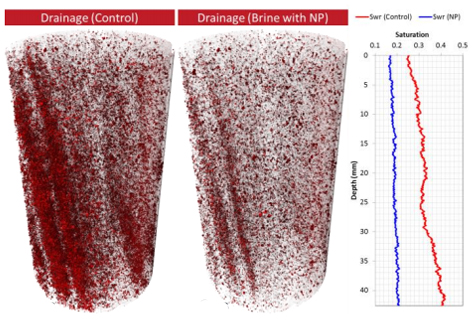
Pore-Scale observations of the effect of surface treated nanoparticles on drainage processes
In this study we observe, using pore scale X-ray micro-CT imaging and advanced petrophysical analysis, how surface treated silica nanoparticles improve sweep efficiency of n-octane in drainage corefloods. Specifically, upon injection of n-octane into a brine saturated core, preferential flow paths are observed and attributed to both viscous instability and rock heterogeneity; when the displaced phase contains a modest volume of nanoparticles, the same preferential flow paths are suppressed re... Read more
Department of Petroleum Engineering, The University of Texas at Austin | Departments of Chemical and Petroleum Engineering, University of Calgary | Materials & Structural Analysis, Thermo Fisher Scientific