Welcome to the PerGeos Use Case Gallery
Below you will find a collection of use cases using PerGeos Software. Based on the technology of its predecessor Avizo Software, PerGeos is a robust software platform for visualizing, processing, and analyzing 2D and 3D digital rock image data.
These use cases include scientific publications, articles, papers, posters, presentations or even videos that show how PerGeos is used to address various scientific and industrial research topics.
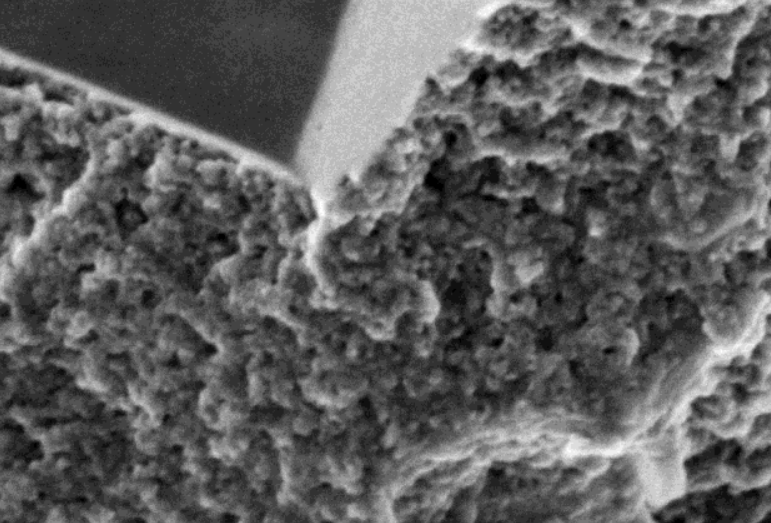
Optimization of production from shale reservoirs requires understanding of rock properties over a range of scales.
Multiple imaging techniques can be combined to determine the nature, connectivity, and wettability of nano-scale pore systems as well as the underlying mineralogy and organic textures that control reservoir behavior and the propensity of the matrix to fail and to contain expulsion cracks. The current study demonstrates new capabilities in integrated multiscale and time-res... Read more
Andrew Fogden, Alession Arena, Christopher Zhang, Ryan T. Armstrong
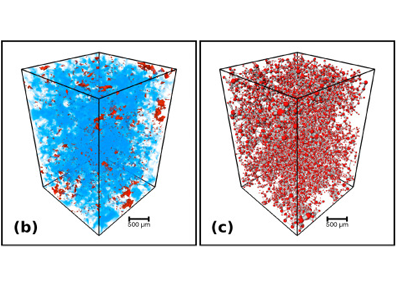
Pore network analysis of Brae Formation sandstone, North Sea
Generating an accurate reservoir model is of critical importance in forecasting the lifespan of hydrocarbon reservoirs and estimating the efficiency of carbon capture and sequestration. One critical parameter controlling the flow of fluids within subsurface reservoirs is the fraction of effective or connected pore spaces in the reservoir. […]
To quantify the connectivity of the pore space, it is therefore necessary to combine high resolution visualization of pore spaces with bulk... Read more
Paul-Ross Thomson; Mark Jefferd; Brett L. Clark; Domenico Chiarella; Tom Mitchell; Saswata Hier-Majumder

Major advance in well bore analysis with CT inspection
Premier, COREX has been providing core analytical services to the oil and gas industry for more than 30 years. Within the last decade it has augmented its rock core investigations by sending samples for analysis approximately every week to Nikon Metrology’s centre of excellence for micro-focus computed tomography (micro-CT) in Tring, Hertfordshire.
Drilling for oil or gas is an expensive business, whether offshore or on land, so it is essential for E&P (exploration and producti... Read more
Nikon
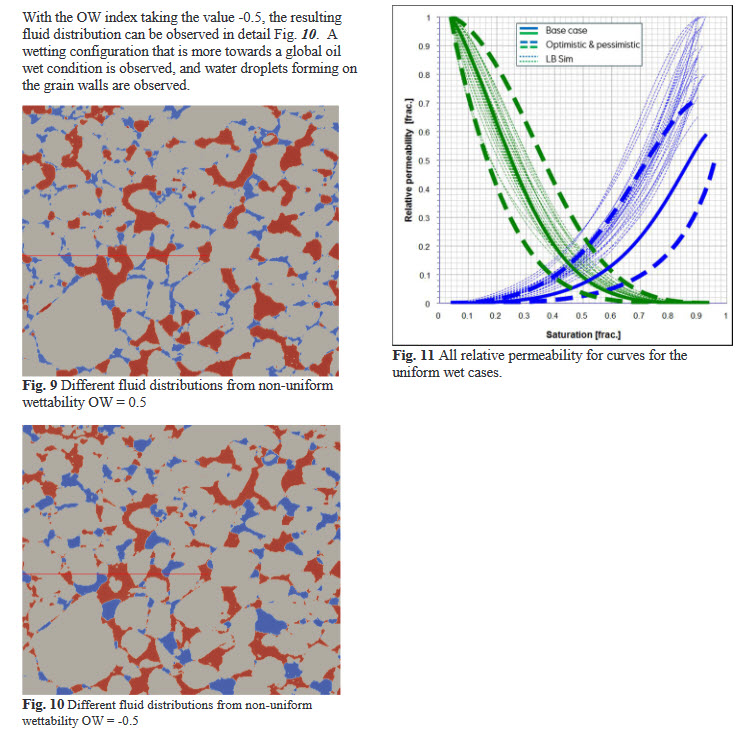
Relative permeability and capillary pressure are key properties within special core analysis and provide crucial information for full field simulation models. These properties are traditionally obtained by multi-phase flow experiments, however pore scale modelling has during the last decade shown to add significant information as well as being less time-consuming to obtain. Pore scale modelling has been performed by using the lattice-Boltzmann method directly on the digital rock models obtain... Read more
ThomasRamstad, Anders Kristoffersen, and EinarEbeltoft
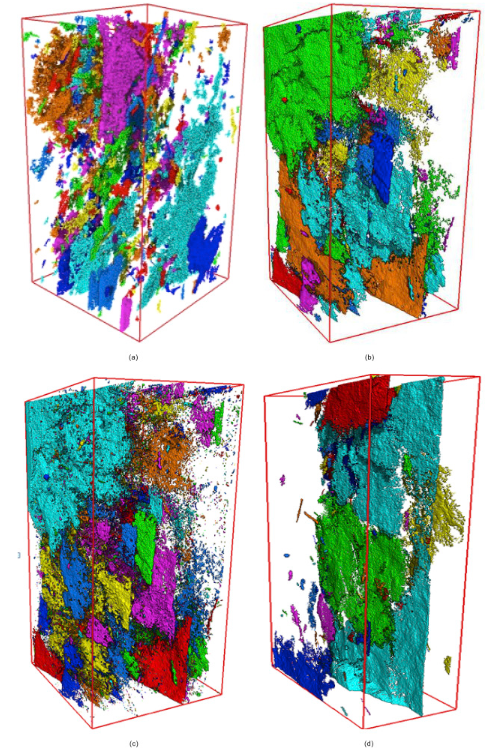
Three-dimensional characterization of micro-fractures in shale reservoir rocks
Fractures are crucial for unconventional hydrocarbon exploitation, but it is difficult to accurately observe the 3D spatial distribution characteristics of fractures. Microtomography (micro-CT) technology makes it possible to observe the 3D structures of fractures at micro-scale. In this study, micron-CT scanning is conducted on multiple mud-shale samples of source rocks in the Permian Lucaogou Formation, Junggar Basin. The Avizo software is applied to process and segment the micron-CT images... Read more
Chao Qi, Xiaoqi Wang, Wei Wang, Jie Liu, Jincai Tuo, Keyu Liu
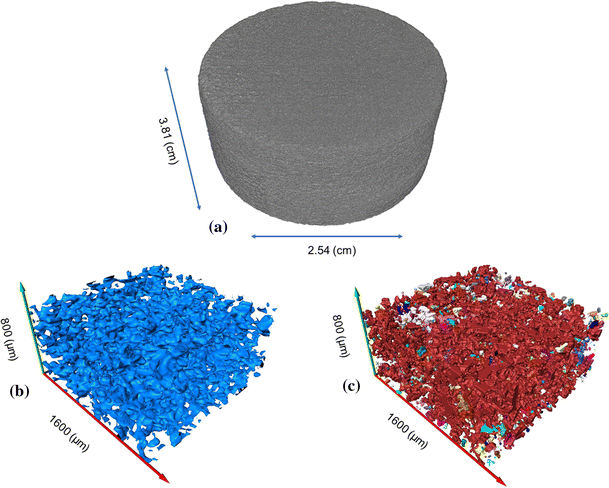
Pore characterization of 3D-printed gypsum rocks: a comprehensive approach
With advancements in additive manufacturing, now 3D-printed core plugs can be duplicated in order to replace natural rock samples. This can help us to control their parameters to be used in different types of experiments for model verifications.
However, prior to such substitutions, we should ensure they can represent natural rock samples through characterizing their physical properties. In this paper, synthetic samples made up of gypsum powder are 3D-printed and then characterized for... Read more
Lingyun Kong, Mehdi Ostadhassan, Chunxiao Li, Naser Tamimi
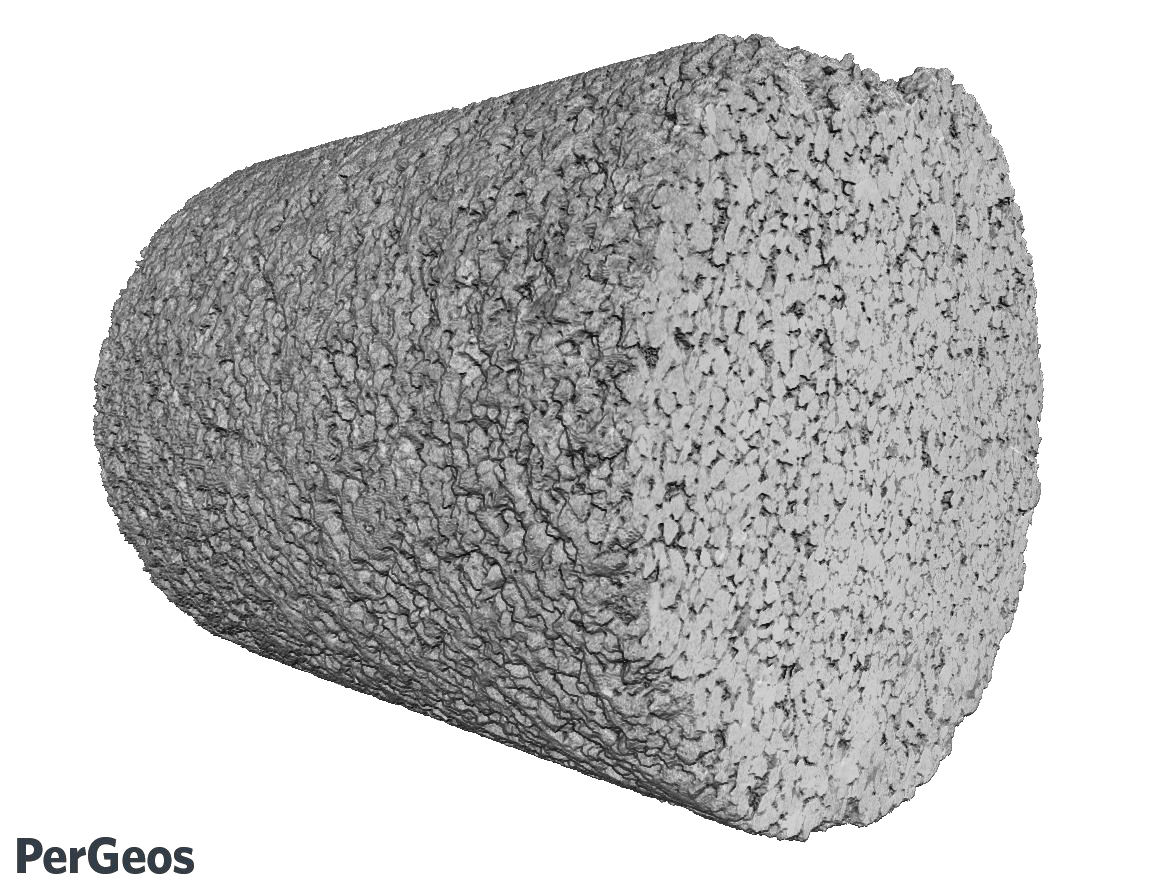

Analyzing Full Micro-CT Image of a Berea Sandstone Mini Plug and the Associated Challenges
X-ray micro-CT imaging is becoming an integral part of rock characterization processes. Large data size, user bias, and accuracy of the results are some of the challenges associated with analyzing micro-CT images of rock samples.
In this article, the PerGeos Digital Rock Analysis software is demonstrated to analyze the full micro-CT dataset of a Berea sandstone mini plug. The analysis is done in blocks using a PerGeos recipe (i.e. a macro) and a block-processing script. The results are... Read more
Arash Aghaei - Thermo Fisher Scientific
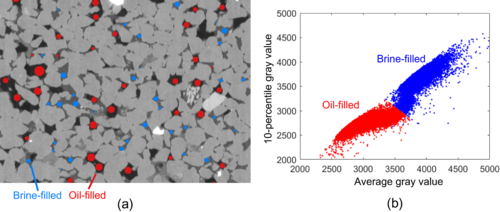
Validation of model predictions of pore-scale fluid distributions during two-phase flow
Pore-scale two-phase flow modeling is an important technology to study a rock’s relative permeability behavior. To investigate if these models are predictive, the calculated pore-scale fluid distributions which determine the relative permeability need to be validated. In this work, we introduce a methodology to quantitatively compare models to experimental fluid distributions in flow experiments visualized with microcomputed tomography.
First, we analyzed five repeated drainage-i... Read more
Tom Bultreys, Qingyang Lin, Ying Gao, Ali Q. Raeini, Ahmed AlRatrout, Branko Bijeljic, and Martin J. Blunt
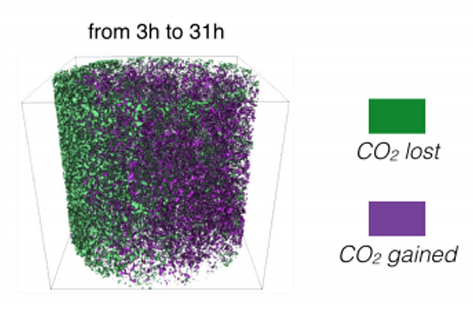
Pore-scale evolution of trapped CO2 at early stages following imbibition using micro-CT imaging
Despite its major influence on storage capacity, CO2 plume migration rate, and rates of CO2 dissolution and mineralization, there are outstanding questions regarding the mechanisms, times scales, influence of geological heterogeneity, and degree of residual trapping. The aim of the present study is to track temporal evolution of residually-trapped scCO2 ganglia during the early stages following imbibition, extract critical parameters such as fluid phase connectivity and scCO2 cluster size an... Read more
Department of Energy Resources Engineering, Stanford University | Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, Earth and Environmental Sciences
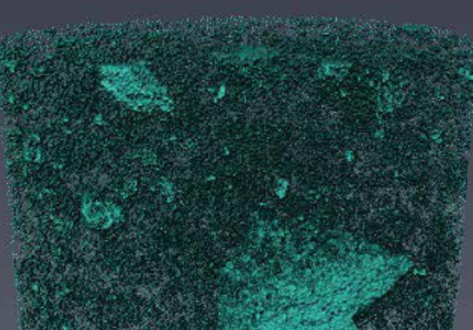
Laboratory Noble Gas Migration Experiments Through Rock
The Underground Nuclear Explosion Signature Experiment (UNESE) is a multi-laboratory effort to improve U.S. capabilities to detect, locate, identify, and characterize underground nuclear explosions. Here we present a lab-scale experiment developed to test advective gas transport though rock samples at in-situ conditions, and results of tests performed at ambient conditions on rocks collected from the site of a field-scale experiment. Gas transport results are compared to pore and fracture net... Read more
Sandia National Laboratories, Los Alamos National Laboratory
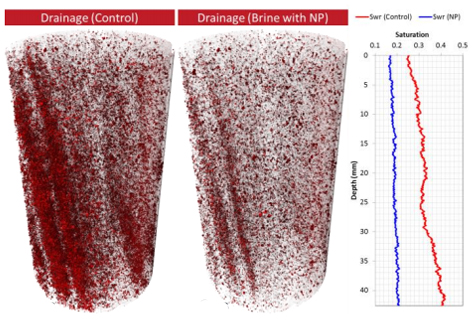
Pore-Scale observations of the effect of surface treated nanoparticles on drainage processes
In this study we observe, using pore scale X-ray micro-CT imaging and advanced petrophysical analysis, how surface treated silica nanoparticles improve sweep efficiency of n-octane in drainage corefloods. Specifically, upon injection of n-octane into a brine saturated core, preferential flow paths are observed and attributed to both viscous instability and rock heterogeneity; when the displaced phase contains a modest volume of nanoparticles, the same preferential flow paths are suppressed re... Read more
Department of Petroleum Engineering, The University of Texas at Austin | Departments of Chemical and Petroleum Engineering, University of Calgary | Materials & Structural Analysis, Thermo Fisher Scientific