Welcome to the PerGeos Use Case Gallery
Below you will find a collection of use cases using PerGeos Software. Based on the technology of its predecessor Avizo Software, PerGeos is a robust software platform for visualizing, processing, and analyzing 2D and 3D digital rock image data.
These use cases include scientific publications, articles, papers, posters, presentations or even videos that show how PerGeos is used to address various scientific and industrial research topics.
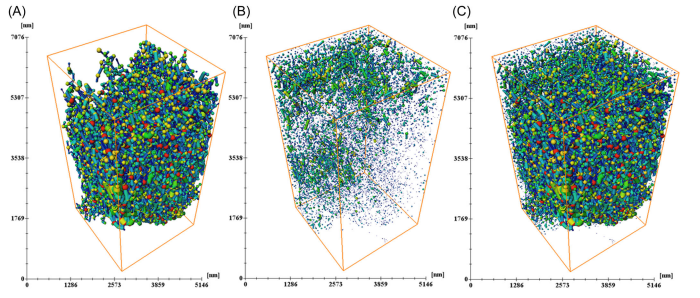
Knowledge of shale pore structure characteristics is crucial to understand gas
storage and seepage mechanisms. Organic matter (OM) pores are considered
the most important pore type in shale, and one of the currently significant
research questions focuses on the spatial distribution and connectivity of OM
pores. To answer this question, typical OM‐rich siliceous shale samples from
the Lower Silurian Longmaxi Formation were comprehensively investigated
usin... Read more
Hui D, Zhang Y, Hu Y, et al.
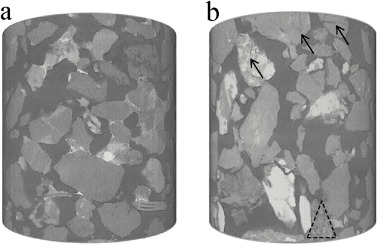
This study investigated the influence of compaction on the variation mechanism of petrophysical properties and the relative permeability of unconsolidated sandstone.
Firstly, triaxial mechanical experiments, CT scans, and mercury injection experiments were performed to analyze the microstructural characteristics and the macroscopic mechanism of changes in the petrophysical characteristics under different pressure. Secondly, a modified permeability test approach was adopted on reservoir... Read more
Yu Xiong, Hongguang Xu, Yongqing Wang, Wensheng Zhou, Ling Wang, Kai Feng
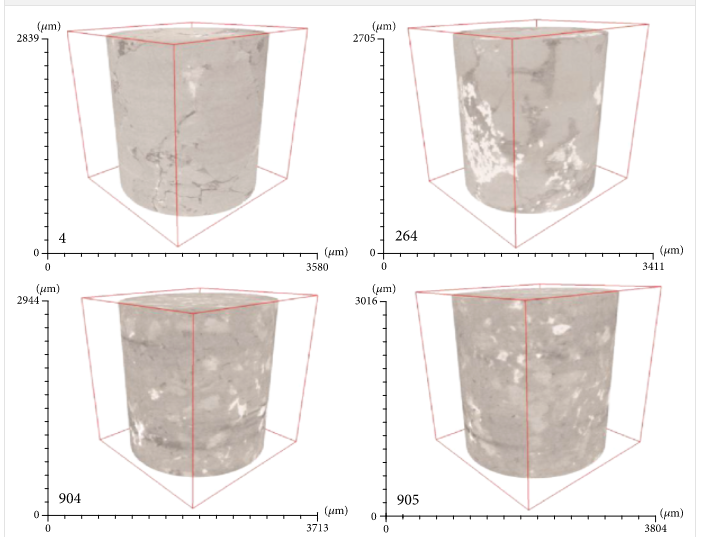
Technological advances and energy demands have made tight sandstone reservoirs worth to be exploited. Tight reservoirs are characterized by low porosity and permeability and strong heterogeneity, especially considering the extensive development of nanometer-scale pore throats or the wide-ranging PSD. Previous studies reveal that the PSD and pore-throat structure have a more direct effect on the storage and transport performance of tight sandstone reservoirs than porosity and permeability. Dif... Read more
Qiang Lei, Liehui Zhang, Hongming Tang, Yulong Zhao, Man Chen, and Chunyu Xie
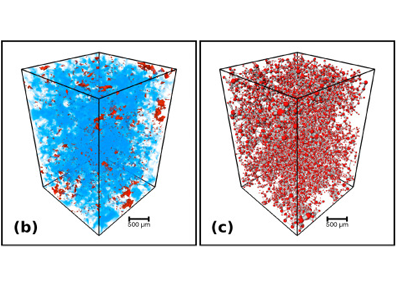
Pore network analysis of Brae Formation sandstone, North Sea
Generating an accurate reservoir model is of critical importance in forecasting the lifespan of hydrocarbon reservoirs and estimating the efficiency of carbon capture and sequestration. One critical parameter controlling the flow of fluids within subsurface reservoirs is the fraction of effective or connected pore spaces in the reservoir. […]
To quantify the connectivity of the pore space, it is therefore necessary to combine high resolution visualization of pore spaces with bulk... Read more
Paul-Ross Thomson; Mark Jefferd; Brett L. Clark; Domenico Chiarella; Tom Mitchell; Saswata Hier-Majumder
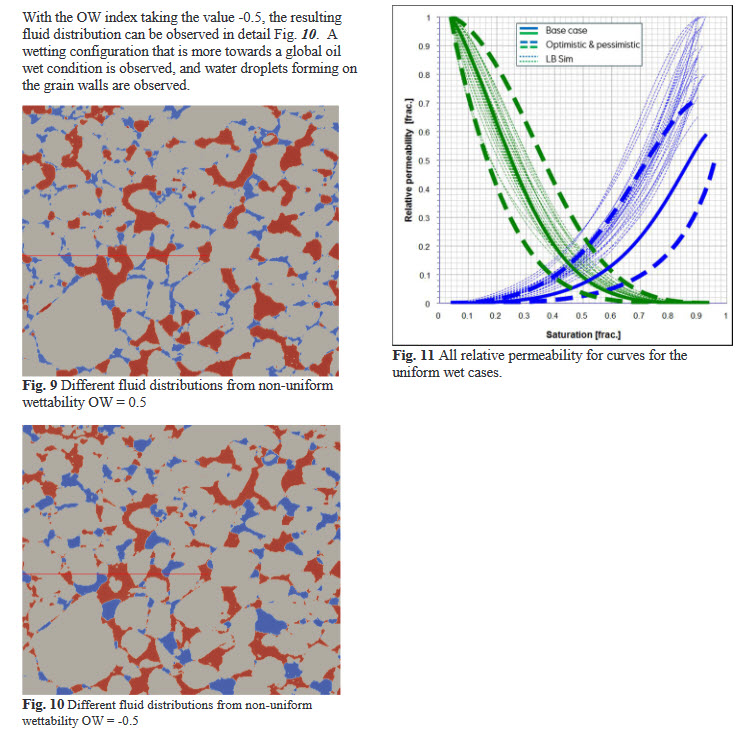
Relative permeability and capillary pressure are key properties within special core analysis and provide crucial information for full field simulation models. These properties are traditionally obtained by multi-phase flow experiments, however pore scale modelling has during the last decade shown to add significant information as well as being less time-consuming to obtain. Pore scale modelling has been performed by using the lattice-Boltzmann method directly on the digital rock models obtain... Read more
ThomasRamstad, Anders Kristoffersen, and EinarEbeltoft
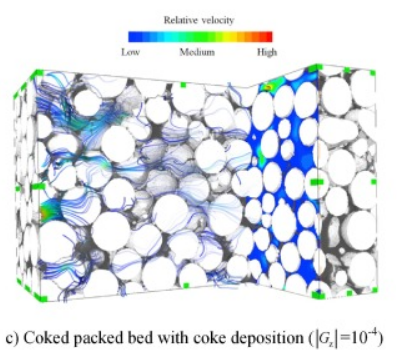
Coke deposition during crude oil in-situ combustion (ISC) is an important phenomenon that significantly impacts the pore topology and permeability.
In this study, X-ray computed microtomography and a specific image processing procedure were used to reconstruct the micro-tomographic images of packed beds with coke deposition. From the reconstructed images, the microstructural parameters related to the transport were analyzed, such as the effective porosity, the constrictivity and the ge... Read more
Qianghui Xu, Wei Long, Hang Jiang, Bin Ma, Cheng Zan, Desheng Ma, Lin Shi
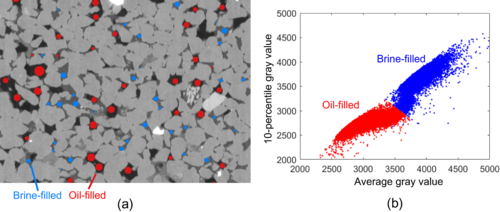
Validation of model predictions of pore-scale fluid distributions during two-phase flow
Pore-scale two-phase flow modeling is an important technology to study a rock’s relative permeability behavior. To investigate if these models are predictive, the calculated pore-scale fluid distributions which determine the relative permeability need to be validated. In this work, we introduce a methodology to quantitatively compare models to experimental fluid distributions in flow experiments visualized with microcomputed tomography.
First, we analyzed five repeated drainage-i... Read more
Tom Bultreys, Qingyang Lin, Ying Gao, Ali Q. Raeini, Ahmed AlRatrout, Branko Bijeljic, and Martin J. Blunt
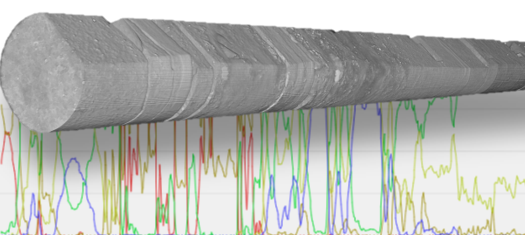
Heterogeneity Logs in PerGeos 1.5
The Core Profile workspace of PerGeos already provides the right tools to visualize logs, CT cores, Bore Hole images and Photographs.
A unique preprocessing step allows the cores barrel to be intelligently removed, the core to be re-oriented if it is not perfectly vertical, and all the cores to be stitched together regardless of the total size.
This allows a user to browse in real time an entire 3D digital well of 100+ cores and apply post-processing operations such as logs gene... Read more
Gwenole Tallec - Thermo Fisher Scientific
Laboratory Noble Gas Migration Experiments Through Rock
The Underground Nuclear Explosion Signature Experiment (UNESE) is a multi-laboratory effort to improve U.S. capabilities to detect, locate, identify, and characterize underground nuclear explosions. Here we present a lab-scale experiment developed to test advective gas transport though rock samples at in-situ conditions, and results of tests performed at ambient conditions on rocks collected from the site of a field-scale experiment. Gas transport results are compared to pore and fracture net... Read more
Sandia National Laboratories, Los Alamos National Laboratory
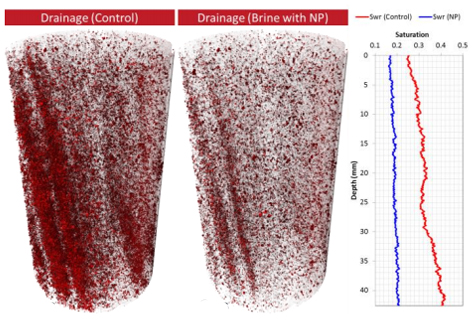
Pore-Scale observations of the effect of surface treated nanoparticles on drainage processes
In this study we observe, using pore scale X-ray micro-CT imaging and advanced petrophysical analysis, how surface treated silica nanoparticles improve sweep efficiency of n-octane in drainage corefloods. Specifically, upon injection of n-octane into a brine saturated core, preferential flow paths are observed and attributed to both viscous instability and rock heterogeneity; when the displaced phase contains a modest volume of nanoparticles, the same preferential flow paths are suppressed re... Read more
Department of Petroleum Engineering, The University of Texas at Austin | Departments of Chemical and Petroleum Engineering, University of Calgary | Materials & Structural Analysis, Thermo Fisher Scientific