Welcome to the PerGeos Use Case Gallery
Below you will find a collection of use cases using PerGeos Software. Based on the technology of its predecessor Avizo Software, PerGeos is a robust software platform for visualizing, processing, and analyzing 2D and 3D digital rock image data.
These use cases include scientific publications, articles, papers, posters, presentations or even videos that show how PerGeos is used to address various scientific and industrial research topics.
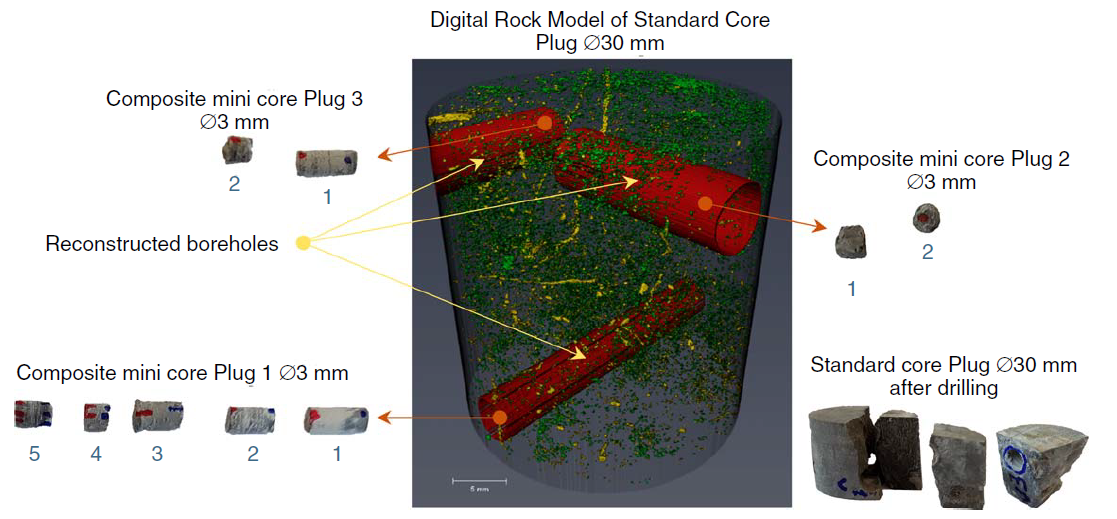
The task of reliable characterization of complex reservoirs is tightly coupled to studying their microstructure at a variety of scales, which requires a departure from traditional petrophysical approaches and delving into the world of nanoscale. A promising method of representatively retaining a large volume of a rock sample while achieving nanoscale resolution is based on multiscale digital rock technology. The smallest scale of this approach is often realized in the form of working with sev... Read more
Andrey Kazak - Svyatoslav Chugunov - Anatolii Chashkov
This study investigated the influence of compaction on the variation mechanism of petrophysical properties and the relative permeability of unconsolidated sandstone.
Firstly, triaxial mechanical experiments, CT scans, and mercury injection experiments were performed to analyze the microstructural characteristics and the macroscopic mechanism of changes in the petrophysical characteristics under different pressure. Secondly, a modified permeability test approach was adopted on reservoir... Read more
Yu Xiong, Hongguang Xu, Yongqing Wang, Wensheng Zhou, Ling Wang, Kai Feng
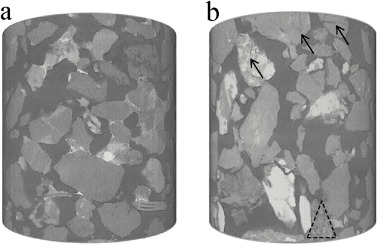
Pore network analysis of Brae Formation sandstone, North Sea
Generating an accurate reservoir model is of critical importance in forecasting the lifespan of hydrocarbon reservoirs and estimating the efficiency of carbon capture and sequestration. One critical parameter controlling the flow of fluids within subsurface reservoirs is the fraction of effective or connected pore spaces in the reservoir. […]
To quantify the connectivity of the pore space, it is therefore necessary to combine high resolution visualization of pore spaces with bulk... Read more
Paul-Ross Thomson; Mark Jefferd; Brett L. Clark; Domenico Chiarella; Tom Mitchell; Saswata Hier-Majumder
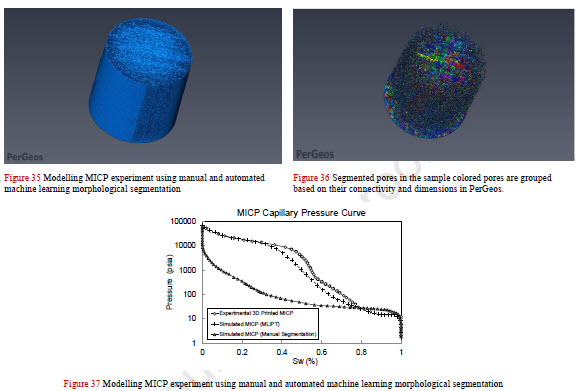
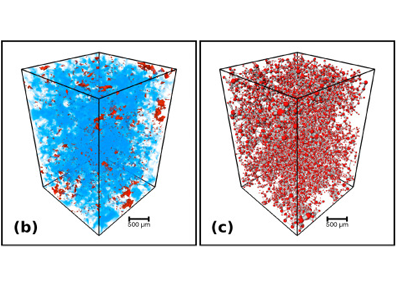
Experimental Investigation of 3D Printed Rock Samples Replicas
Laboratory Experiments on rock specimens are designed for understanding and characterizing subsurface environment, quantifying potential recovery, and tuning fluid flow models in porous media. The spatial variability and reservoirs’ heterogeneities predicate acquiring expensive cores from different locations. These experiments are mechanically and petrophysically destructive and cannot be repeated or extended on the same core. Replicating core samples with 3D-printing technology innovation ... Read more
Ahmed G.Almetwally, H.Jabbari
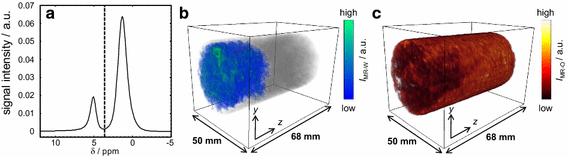
Accurate monitoring of multiphase displacement processes is essential for the development, validation and benchmarking of numerical models used for reservoir simulation and for asset characterization.
Here we demonstrate the first application of a chemically-selective 3D magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) technique which provides high-temporal resolution, quantitative, spatially resolved information of oil and water saturations during a dynamic imbibition core flood experiment in an Esta... Read more
N. P. Ramskill, A. J. Sederman, M. D. Mantle, M. Appel, H. de Jong, L. F. Gladden
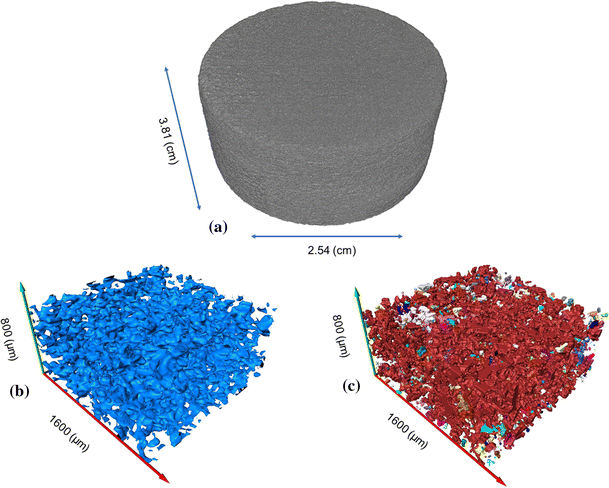
Pore characterization of 3D-printed gypsum rocks: a comprehensive approach
With advancements in additive manufacturing, now 3D-printed core plugs can be duplicated in order to replace natural rock samples. This can help us to control their parameters to be used in different types of experiments for model verifications.
However, prior to such substitutions, we should ensure they can represent natural rock samples through characterizing their physical properties. In this paper, synthetic samples made up of gypsum powder are 3D-printed and then characterized for... Read more
Lingyun Kong, Mehdi Ostadhassan, Chunxiao Li, Naser Tamimi
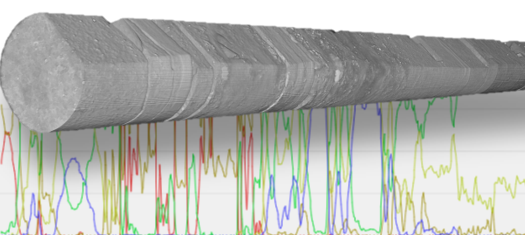
Heterogeneity Logs in PerGeos 1.5
The Core Profile workspace of PerGeos already provides the right tools to visualize logs, CT cores, Bore Hole images and Photographs.
A unique preprocessing step allows the cores barrel to be intelligently removed, the core to be re-oriented if it is not perfectly vertical, and all the cores to be stitched together regardless of the total size.
This allows a user to browse in real time an entire 3D digital well of 100+ cores and apply post-processing operations such as logs gene... Read more
Gwenole Tallec - Thermo Fisher Scientific
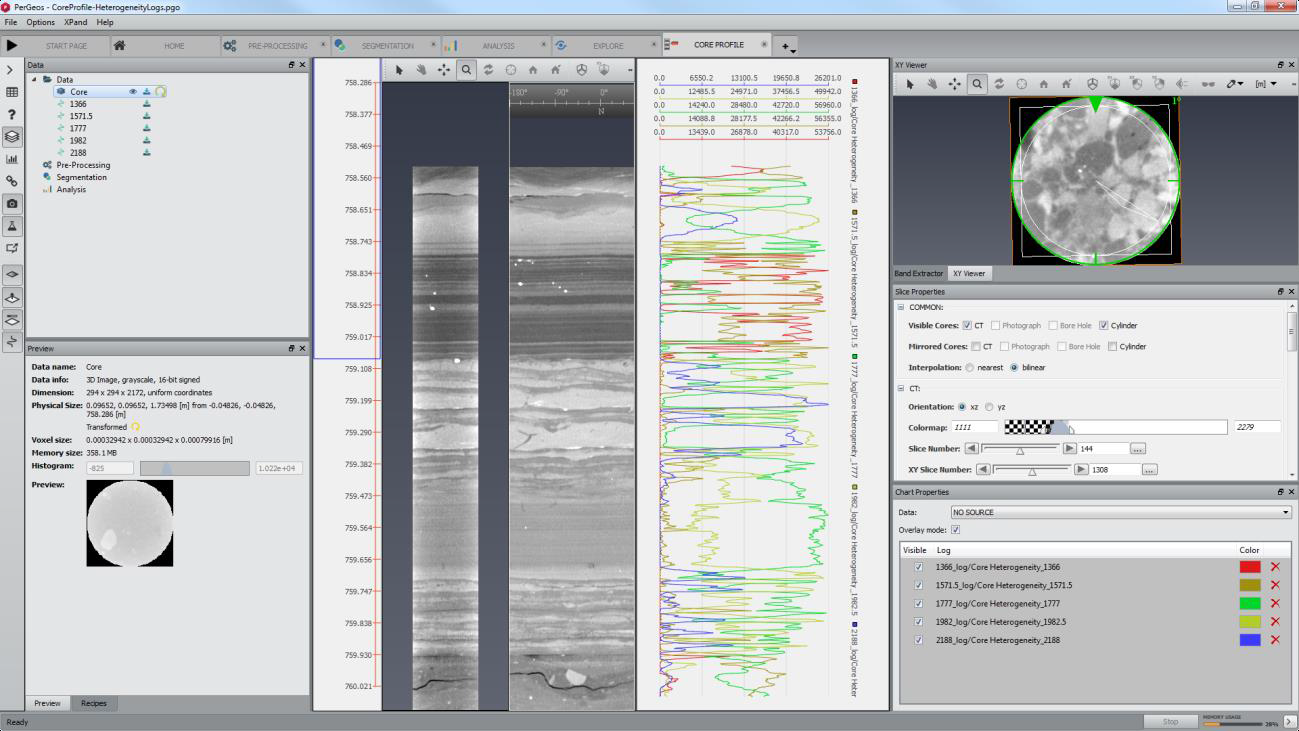
Improving Whole Core Characterization with Automated Log Generation in PerGeos
The Core Profile Extension, available for PerGeos, provides a powerful toolset for visualization and analysis of whole core CT data. Within this extension the user can load and visualize an entire wells worth of CT data as well as performing detailed analysis of geological and chemical features by utilizing the powerful image analysis library fundamental to PerGeos.
In this example, we illustrate the usefulness of core profile in augmenting traditional core analysis routines and provid... Read more
Gwenole Tallec - Thermo Fisher Scientific
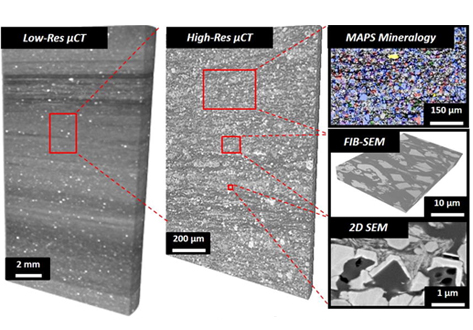
The complexity of unconventional rock systems is expressed both in the compositional variance of the microstructure and the extensive heterogeneity of the pore space. Visualizing and quantifying the microstructure of oil shale before and after pyrolysis permits a more accurate determination of petrophysical properties which are important in modeling hydrocarbon production potential. We characterize the microstructural heterogeneity of oil shale using X-ray micro-tomography (µCT), automated u... Read more
Imperial College London, Tarik Saif, Qingyang Lin, Alan R.Butcher, Branko Bijeljic, Martin J.Blunt
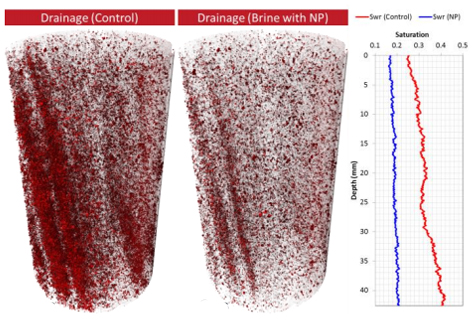
Pore-Scale observations of the effect of surface treated nanoparticles on drainage processes
In this study we observe, using pore scale X-ray micro-CT imaging and advanced petrophysical analysis, how surface treated silica nanoparticles improve sweep efficiency of n-octane in drainage corefloods. Specifically, upon injection of n-octane into a brine saturated core, preferential flow paths are observed and attributed to both viscous instability and rock heterogeneity; when the displaced phase contains a modest volume of nanoparticles, the same preferential flow paths are suppressed re... Read more
Department of Petroleum Engineering, The University of Texas at Austin | Departments of Chemical and Petroleum Engineering, University of Calgary | Materials & Structural Analysis, Thermo Fisher Scientific